Peer Learning is...
Defining Responsiveness
Responsiveness |rɪˈspɒnsɪvnəs|
noun [mass noun]A learning environment's ability to systematically assess and provide knowledge as and when it is needed by the learner..
Learners, especially those who are learning as they go, are all different. Lock them to a preset path based on predicted needs creates resistance and awkward disconnects. For example:
- You might have a great class advertised about writing short stories, but you assumed most participants would be new to creative writing. When you start, you find out half of them have publishers or are releasing their second and third books.
- You might think that inserting your business workshop is what's needed for a bunch of techies, but they don’t see the point of learning “the business side.”
Assess then intervene
Responsiveness is achieved by systematically assessing the learner's needs, goals and perspectives, and then intervening in the learning program.
Calibrated & Modular
A simple form of Responsiveness is to ask the learners what topics or aspects of a topic they'd like to learn, and then anticipate their questions.
In this form, a given workshop or lecture can be split into modules, depending on skill level or context, so that the instructor can choose appropriately based on the learners' questions.

Through calibrated assessment you can for instance see a lack of financial literacy with learners, and tag the specific topics that they're missing. Or, it could be that learners don't see yet why cashflow management is not only important to prevent your business from going bankrupt, but that timing of payments coming in and going out can also facilitate the operation of your business.
For intervention that follows, it is sufficient to anticipate different learning needs, and prepare a range of content options. For example, a modular film-making workshop would include basics, like planning and story-boarding, and a choice of more advanced topics, like mixing genres or adlibbing dialogue. This allows the facilitator to choose which modules are appropriate to the learners, and deploy them as needs arise.
Systematic calibration is one half of responsiveness. But knowing each learner's needs doesn't lead to relevant education unless the program can systematically adapt and respond to them.
The other half is planning for an appropriate intervention. At this starting level of Responsiveness, the intervention is a pre-selected tool, like a workshop, that needs to be calibrated to the learners beforehand.
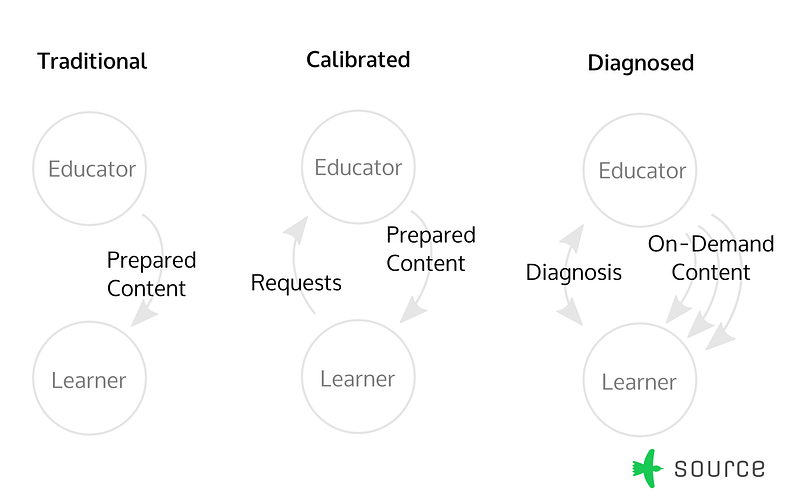
Diagnostic & Open-Ended
More sophisticated forms of Responsiveness are able to react appropriately without prepared content. This reponse is built on deeper, and more refined diagnoses of learners needs.
The methods used for diagnosis tend to be based on conversations between learners, and mentors, experts, and also amongst learners themselves. These conversations give a broad perspective on the learners about where they are, and their priorities.
The range of learning topics that emerges from diagnosis is diverse, and specific to each learner. But by performing diagnosis on a systemic basis, the learners' needs converge into learning topics.
The interventions are open-ended. But they can rely on guidance by the learning topics to gather people to work on solutions. These gatherings include a wide range domain experts to cater to the diveristy of learning topics.
For example, an experienced facilitator running a "campfire discussion" assesses the stage and interest of the participants, and then directs relevant experts among them - to tell useful stories or coach others through their challenges.
Or, a startup mentor can foresee a first-time founder's next big challenge, and introduce them to someone who will help them navigate it.
A learning environment's Responsiveness can be described as either:
Level 0 : Ignorant. The form and content of education are predetermined and unchanging in the face of exposed learning needs.
Level 1 : Adaptive. Learners are invited to ask questions, and state learning goals at the start of, and during the learning experience. These questions are responded to by selecting from pre-determined modules that allow for some variance in delivery from the major predetermined content.
Level 2 : Diagnostic. Learners needs are proactively and deeply assessed through activities such as mentoring, usually before the learning experience. The program plans on open-ended forms of education, allowing the appropriate style of knowledge transfer to be chosen.
Peer Learning environments are able to assess learning needs through mentoring interactions between its peer constituents, and respond to them by involving relevant expertise.
